PLYWOOD
Plywood is a sheet material manufactured from thin layers or “plies” of wood veneer that are glued together with adjacent layers having their wood grain rotated up to 90 degrees to one another.All plywood bind resin and wood fibre sheets (cellulose cells are long, strong and thin) to form a composite material. The alternation of the grain is called cross–graining and has several important benefits: it reduces the tendency of wood to split when nailed at the edges; it reduces expansion and shrinkage, providing improved dimensional stability; and it makes the strength of the panel consistent across all directions.

SPECIFICATIONS
THICKNESS SIZE
1⁄8 to 3.0 in 4’x8’
(3.2 to 76.2mm) (1200x1400mm)
Sheet weight of ½” thick softwood plywood – 18kgs
Sheet weight of ½” thick hardwood plywood – 20kgs
APPLICATIONS
Typical end uses of softwood plywood are:
- Floors, walls and roofs in home constructions
- Wind bracing panels
- Vehicle internal body work
- Packages and boxes
- Fencing
SPECIFICATIONS
THICKNESS SIZE
1⁄8 to 3.0 in 4’x8’
(3.2 to 76.2mm) (1200x1400mm)
Sheet weight of ½” thick softwood plywood – 18kgs
Sheet weight of ½” thick hardwood plywood – 20kgs
APPLICATIONS
Typical end uses of softwood plywood are:
- Floors, walls and roofs in home constructions
- Wind bracing panels
- Vehicle internal body work
- Packages and boxes
- Fencing



Typical end uses of hardwood plywood are:
- Panels in concrete form work systems
- Floors, walls and roofs in transport vehicles
- Container floors
- Floors subjected to heavy wear in various buildings and factories
- Scaffolding materials
- Interior finishes


TYPES OF PLYWOOD
SOFTWOOD PLYWOOD
Softwood panel is usually made either of cedar, Douglas fir or spruce, pine, and fir (collectively known as spruce-pine-fir or SPF) or redwood and is typically used for construction and industrial purposes.
HARDWOOD PLYWOOD
Hardwood plywood is made out of wood from angiosperm trees and used for demanding end uses. Hardwood plywood is characterized by its excellent strength, stiffness and resistance to creep. It has a high planar shear strength and impact resistance, which make it especially suitable for heavy-duty floor and wall structures.
TROPICAL PLYWOOD
Tropical plywood is made of mixed species of tropical wood. Originally from the Asian region, it is now also manufactured in African and South American countries. Tropical plywood is superior to softwood plywood due to its density, strength, evenness of layers, and high quality.It is the preferred choice for construction purposes in many regions due to its low cost.
AIRCRAFT PLYWOOD
High-strength plywood also known as aircraft plywood, is made from mahogany and/or birch, and uses adhesives with increased resistance to heat and humidity. It was used for several World War II fighter aircraft.
DECORATIVE PLYWOOD
It is usually faced with hardwood, including ash, oak, red oak, birch, maple, mahogany, Philippine mahogany, rosewood, teak and a large number of other hardwoods.
MARINE PLYWOOD
Marine plywood is manufactured from durable face and core veneers, with few defects so it performs longer in both humid and wet conditions and resists delaminating and fungal attack. Its construction is such that it can be used in environments where it is exposed to moisture for long periods. Each wood veneer will be from tropical hardwoods, have negligible core gap, limiting the chance of trapping water in the plywood and hence providing a solid and stable glue bond.
POPULAR PLYWOOD BRANDS IN INDIA
- CENTURY PLYBOARDS LTD.
– GREENPLY INDUSTRIES LTD.
– ARCHIDPLY INDUSTRIES LTD.
– SARDA PLYWOOD INDUSTRIES LTD.
– UNIPLY INDUSTRIES LTD.
REFERENCE
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mcSn9HvQ4AU
MEDIUM DENSITY FIBRE (MDF)
Medium-density fibreboard (MDF) is an engineered wood product made by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into wood fibres, often in a defibrator, combining it with wax and a resin binder, and forming panels by applying high temperature and pressure.

MDF is generally denser than plywood and much denser and stronger than particle board. MDF does not contain knots or rings, making it more uniform than natural woods during cutting and in service. MDF may be glued, doweled or laminated.
SPECIFICATIONS
MDF is made up of 82% wood fibre, 9% urea-formaldehyde resin glue, 8% water and 1% paraffin wax.
THICKNESS SIZE
2 mm 1220x915mm
2.5mm 1515x1220mm (or) 1220x915mm (or) 1830x1220mm (or) 2500x1240mm
3 mm 1220x915mm (or) 1830x1220mm (or) 2440x1220mm
6mm 2440x1220mm
12mm 2440x1220mm
BENEFITS
- Is an excellent substrate for veneers.
- Some varieties are less expensive than many natural woods
- Isotropic (its properties are the same in all directions as a result of no grain), so no tendency to split
- Shapes well, stable dimensions, easy to finish.
DRAWBACKS
- Denser than plywoodor chipboard (the resins are heavy).
- May warp or expand if not sealed.
- Low grade MDF may swell and break when saturated with water.
- Though it does not have a grain in the plane of the board, it does have one intothe board. Screwing into the edge of a board will generally cause it to split in a fashion similar to delaminating.
Veneered MDF provides many of the advantages of MDF with a decorative wood veneer surface layer. In modern construction, spurred by the high costs of hardwoods, manufacturers have been adopting this approach to achieve a high quality finishing wrap covering over a standard MDF board.
APPLICATIONS
MDF is often used in school projects because of its flexibility.
- Slat wallPanels made from MDF are used in the shop fitting
- Primarily used for internal applications due to its poor moisture resistance. It is available in raw form with fine sanded surface or with decorative overlay.
- MDF is also usable for furniture such as cabinets, because of its strong surface.


REFERENCE
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZRE1L7anoss
HIGH DENSITY FIBRE (HDF)
It is made out of exploded wood fibres that have been highly compressed. It is similar to particle board and medium-density fibreboard, but is denser and much stronger and harder.

It differs from particle board in that the bonding of the wood fibres requires no additional materials, although resin is often added. The hardboard variety is made without resin. The HDF version is made with resin. Unlike particle board, it will not split or crack.
SPECIFICATION
THICKNESS SIZE
2070x2620mm
1220x2725mm
2.0 to 25mm 1220x2440mm
1525x2440mm
1525x2725mm
APPLICATIONS
- It is widely used in indoor and outdoor decoration, office and high-grade furniture, stereos, interior decoration of senior cars and electronics industry.
- It also serves as good production materials for antistatic flooring in computer rooms, wall defence clapboard, burglarproof door, wall panels, and shelves and so on.
- It is also a fine packaging material.
- It is widely used in interior decoration in place of high-class hardwood and can be directly processed into composite floor, strengthened wood flooring etc.


REFERENCE
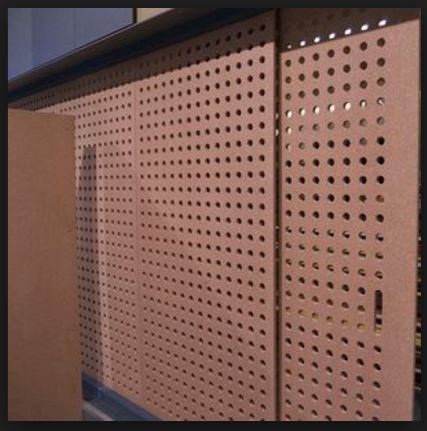
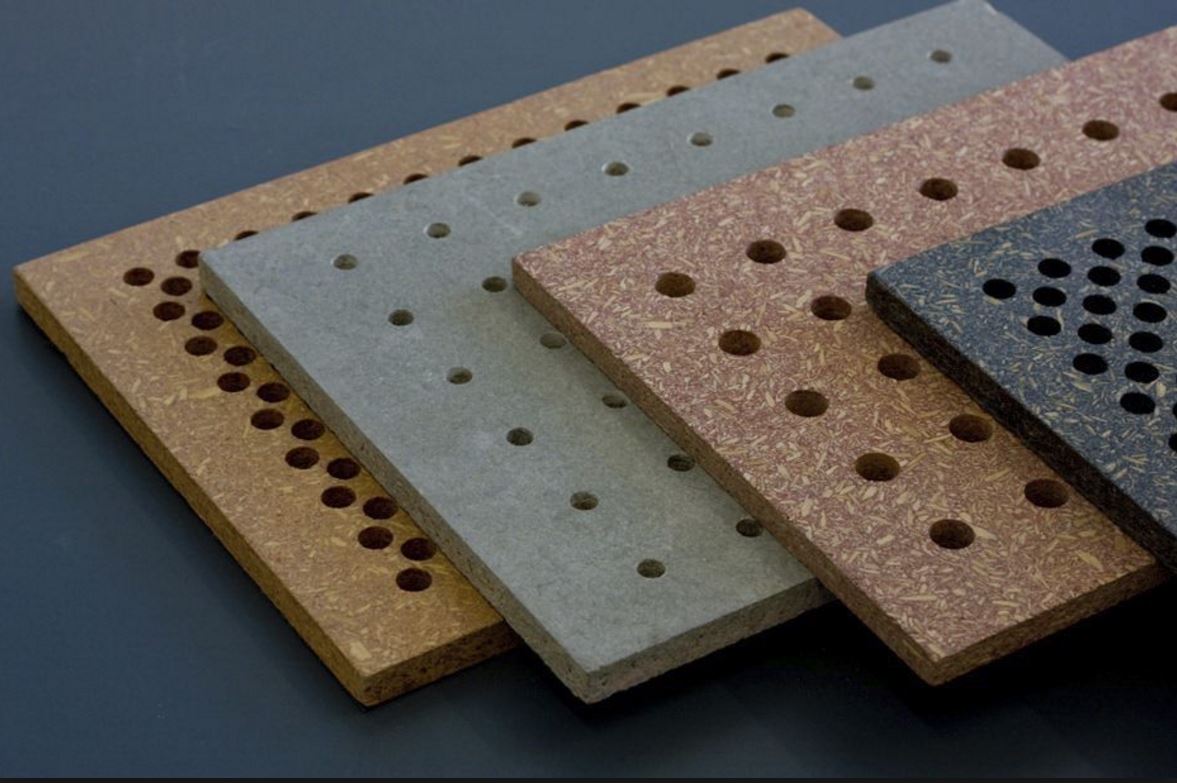
PARTICLE BOARD
Particleboard, also known as chipboard, is an engineered wood product manufactured from wood chips, sawmill shavings, or even sawdust, and a synthetic resin or other suitable binder, which is pressed and extruded. Particleboard or chipboard is manufactured by mixing wood particles or flakes together with a resin and forming the mixture into a sheet. The raw material to be used for the particles is fed into a disc chipper with between four and sixteen radially arranged blades (the chips from disk chippers are more uniform in shape and size than from other types of wood chipper). The particles are then dried, after which any oversized or undersized particles are screened out.

SPECIFICATION
The thickness of particleboard shall be 4 mm 6 mm 9 mm 12 mm 15 mm 20 mm 25 mm 30 mm 35 mm, 40 mm and 50 mm.
THICKNESS SIZE APPROX SHEET WEIGHT
12mm 2400x1200mm 29 kgs
16mm 2400x1200mm 33 kgs
18mm 2400x1200mm 37kgs
18 mm 2700x900mm 31kgs
BENEFITS
- Particle board is cheaper,denser and more uniform than conventional wood and plywood and is substituted for them when cost is more important than strength and appearance.
- The advantages of using particleboard over veneer core plywood is it is more stable, much cheaper to buy, and somewhat more convenient to use.
- Particleboard is slick, smooth and very flat. For this reason, it is commonly used for floor underlay. Glue adheres to it readily and tile, linoleum or even hardwood can be placed on top of it with good results.
DRAWBACKS
- A major disadvantage of particleboard is that it is very prone to expansion and discoloration due to moisture, particularly when it is not covered withpaint or another sealer.
- Particleboard will absorb moisture, causing it to swell. This can be a problem if excessive water is spilled on linoleum, carpet, hardwood or anywhere that particleboard is used as a floor underlay.
- Particle boards cannot be used in applications where the boards will be subjected to heavy weights. Being low on strength, particle boards are only suitable for holding low weights, or as forming the walls of cabinets and the like.
APPLICATIONS
- Particle board comes in several thicknesses which make it a versatile enough product to be used in roofing. Treated lumber is often used as the main material with thin sheets of treated particle board being placed on top and then shingles are attached. This is especially common on a low-slope roof.
- Due to the durability of particle board it is sometimes used an added insulating Other products are used in conjunction with it to keep heat loss and moisture at a minimum.
- The material absorbs sound and does not bounce it back. This is why particle board is use in walls and floors in recording studios, concert halls and media rooms.
- There are many areas of the home that can be spruced up by adding accent pieces. The most popular place for accents are around windows, doors, floor and ceiling in the form of trim and moulding. These materials are made cheaper when they are created from particle board.
REFERENCE
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BSmv0dXaiMI
Essay assistance https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2021/03/24/2198954/0/en/4-Best-Research-Paper-Writing-Services-Top-USA-Paper-Writers-Among-69-Tested-Review-by-Halvorson.html can be useful due to the knowledge you gain from the experience.